NewsDetails
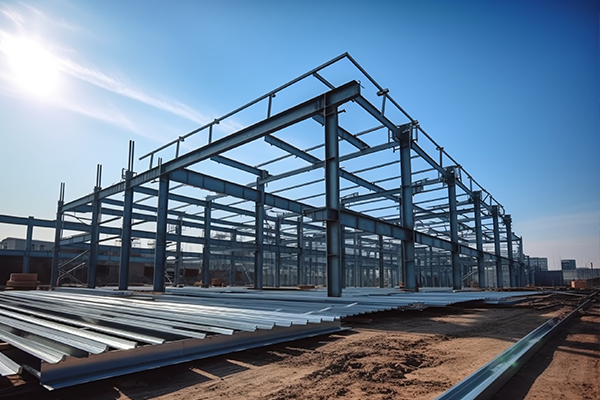
H-Beam vs I-Beam vs C-Channel: Key Differences and Selection Guide for Steel Structures
author:Tianxing time:2025-04-03 13:26:50 Click:66
1. Core Differences Between the Three Profiles
1. Cross-Sectional Shapes & Structural Features
| Profile | Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
| H-Beam | Wide, equal-thickness flanges; right-angle web-flange connection; "H"-shaped section | |
| I-Beam | Narrow, tapered flanges; thicker web; "I"-shaped section | |
| C-Channel | Open-sided, lipped channel; lightweight "C"-shaped section |
Key Distinctions:
Flange Width: H-Beam > I-Beam > C-Channel
Bending Resistance: H-Beam (bidirectional) > I-Beam (unidirectional) > C-Channel (local load-bearing)
Connection Methods: H/I-beams use welding/bolting; C-channels often use self-tapping screws.
2. Mechanical Properties Comparison
| Property | H-Beam | I-Beam | C-Channel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bending Strength | High (uniform bidirectional) | Moderate (axial) | Low (requires assembly) |
| Compression Resistance | Excellent (wide-flange stability) | Good (web support) | Poor (needs reinforcement) |
| Torsional Resistance | Moderate | Low | Very Low |
Typical Applications:
H-Beam: Long-span factory frames, high-rise steel columns/beams
I-Beam: Secondary beams, crane beams, unidirectional load components
C-Channel: Lightweight partitions, roof purlins, temporary structures
3. Cost & Installation Efficiency
| Factor | H-Beam | I-Beam | C-Channel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Price | Higher (material-efficient) | Moderate | Lowest |
| Fabrication Complexity | Requires professional cutting/welding | High welding precision | On-site assembly possible |
| Transport Cost | High (heavy single pieces) | Moderate | Low (bundlable) |
2. Selection Guide: How to Choose Based on Project Needs?
Choose H-Beam When:
High load-bearing capacity is needed (e.g., high-rise columns, heavy industrial main beams).
Bidirectional force distribution (e.g., seismic-resistant structures).
Long spans (>15m): Superior stability vs I-beams.
Choose I-Beam When:
Unidirectional bending (e.g., secondary beams, equipment supports).
Mid/small-scale projects with budget constraints: Generally cheaper than H-beams.
Dynamic loads (e.g., crane beams): Thicker webs resist shear forces.
Choose C-Channel When:
Lightweight enclosures (e.g., roof purlins, partition studs).
Fast installation: Prefabricated, easy on-site assembly.
Temporary/low-load structures (e.g., site shelters, warehouse mezzanines).
3. FAQ
❓ Q1: Can H-beams and I-beams be used interchangeably?
→ Not recommended! H-beams handle bidirectional forces better; substitution may compromise stability.
❓ Q2: Why can’t C-channels be used for primary load-bearing?
→ Open sections lack torsional resistance; must combine with square tubes/H-beams.
❓ Q3: How to reduce H-beam costs?
→ Optimize design (e.g., reduce web height); choose standard sizes (custom sizes cost more).
4. Conclusion
Material selection should balance load requirements, span, budget, and construction conditions. As a professional steel structure manufacturer, we offer free consultation + 3D structural simulations—contact our engineers for solutions ↓
 Recommended Products
Recommended Products
 Contact us
Contact us
—— Contact:Ms. Zhang
—— Tel:(+86)18399688883
—— Email:18399688883@163.com
—— Url:https://www.tianxingmaterials.com
—— Address:Horgos City, Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang, China